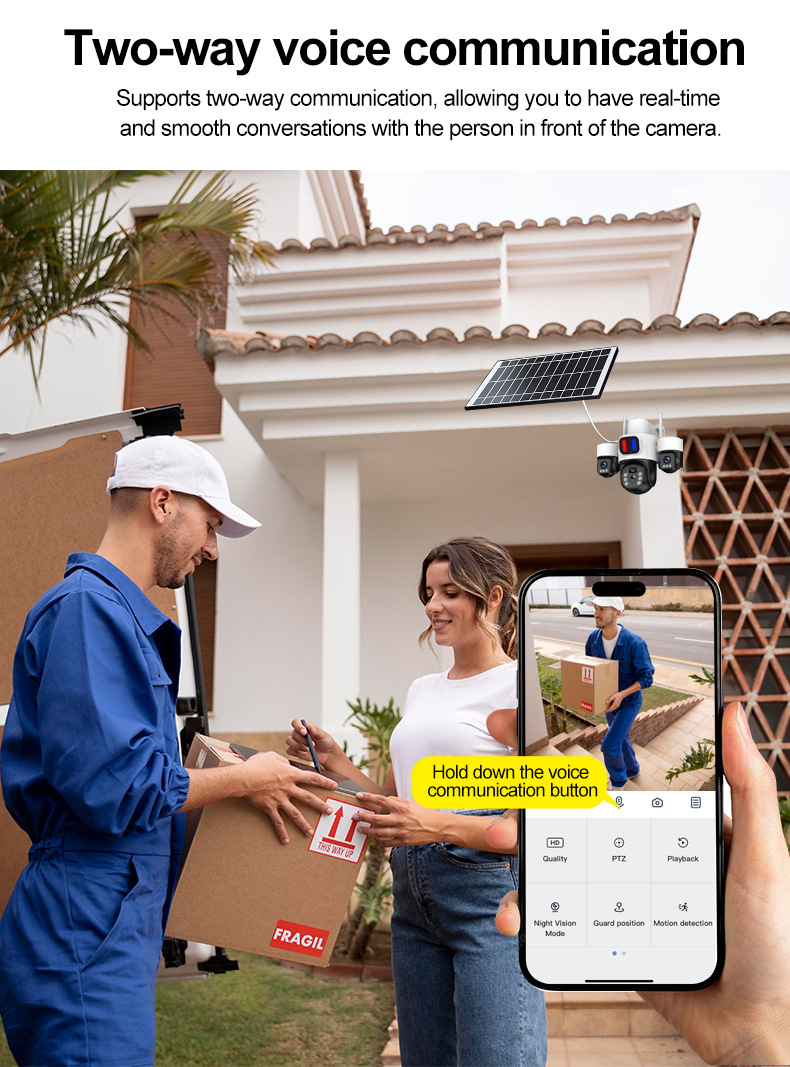
Off-Grid Solar-Powered Multi-Lens Surveillance Camera System with Active Deterrence
Engineering Conclusion
This off-grid solar-powered multi-lens surveillance camera system with active deterrence is engineered for remote and unattended sites where simultaneous multi-directional visual coverage and immediate on-site response are required under constrained energy conditions.
System suitability is determined by coverage continuity, response latency tolerance, and energy autonomy management, rather than by lens count or deterrence output alone.
Engineering Problem This System Addresses
In many off-grid surveillance deployments, critical events occur unpredictably and often outside the viewing direction of a single camera or the rotation window of a PTZ system.
Mechanical repositioning introduces response latency, while blind zones increase missed-detection risk—especially in high-risk or unattended environments.
This system addresses these challenges by combining fixed multi-lens optical coverage, autonomous power supply, and event-driven active deterrence, reducing reliance on mechanical movement and external response workflows.
System Architecture Overview
The system integrates photovoltaic generation, onboard energy storage, multi-lens visual sensing, and active deterrence mechanisms into a unified off-grid platform.
Each optical channel provides continuous directional awareness, while power generation, storage, and response logic are coordinated through centralized energy-aware control.
By distributing visual responsibility across multiple lenses, the architecture minimizes mechanical dependency and enables consistent situational awareness without continuous PTZ actuation.
Why Multi-Lens Architecture Matters in Off-Grid Surveillance
Multi-lens architecture enables simultaneous monitoring of multiple directions, eliminating coverage gaps caused by camera rotation or delayed repositioning.
This is particularly critical in environments where events are brief, unpredictable, or concurrent across different zones.
Unlike PTZ-centric systems, multi-lens configurations preserve coverage continuity even during response escalation, ensuring that deterrence actions do not compromise ongoing observation.
Role of Active Deterrence in Multi-Lens Deployments
Active deterrence provides an immediate response layer that operates independently of camera orientation.
When integrated into a multi-lens system, deterrence can be triggered by any optical channel without waiting for mechanical alignment or operator intervention.
This decoupling reduces response latency and enhances system effectiveness in environments where delayed human response increases operational risk.
Engineering Boundary Conditions & Design Assumptions
This system is designed and validated under the following engineering boundary conditions, which define operational applicability:
✅ Grid Availability Constraint
Intended for locations without stable grid access or where cabling and trenching introduce unacceptable cost or reliability risk.
✅ Solar Resource Assumption
Energy autonomy calculations are based on realistic daily solar irradiation patterns observed across diverse geographic regions rather than peak laboratory values.
✅ Energy Variability Window
System operation accounts for extended low-generation periods, during which prioritized optical coverage and response logic are maintained.
✅ Environmental Exposure Limits
Designed for outdoor deployment under wind, dust, rainfall, and temperature conditions typical of rural infrastructure, construction zones, and remote assets.
✅ Maintenance Access Constraint
Optimized for long inspection intervals where reactive maintenance access is limited or costly.
Decision-Relevant Parameters
The following parameters are presented as engineering decision variables rather than isolated specifications:
Optical Channel Allocation
Lens count and orientation are selected to balance coverage density with energy consumption, ensuring continuous multi-directional awareness without excessive power draw.
Energy Storage Capacity
Battery sizing supports simultaneous multi-lens operation and event-driven deterrence during extended low-irradiance periods.
Power-Aware Control Logic
System logic prioritizes essential optical channels and response functions under constrained energy conditions to preserve baseline surveillance continuity.
Deterrence Activation Strategy
Deterrence output is designed for event-triggered operation rather than continuous signaling, preventing unnecessary energy depletion.
Integrated System Architecture
Consolidation of sensing, power, and response functions reduces external wiring and minimizes long-term failure points in outdoor deployments.
Engineering Decision Rationale
From an engineering decision perspective, this architecture is selected to reduce missed-detection risk and response latency, rather than to maximize component counts:
✅ Multi-lens coverage eliminates blind zones inherent to single-axis observation
✅ Reduced mechanical dependence improves reliability in unattended environments
✅ Active deterrence shortens the gap between detection and response
✅ Energy autonomy governs system effectiveness more than nominal output ratings
✅ Power-aware prioritization preserves long-term operational stability
Engineering Comparison: Multi-Lens vs PTZ vs Camera-Only Systems
This comparison addresses engineering decision trade-offs, not feature lists, between three common off-grid surveillance architectures.
Primary Engineering Objective
Camera-Only SystemsOptimized for evidence capture and passive monitoring where response actions are handled remotely and coverage direction is predictable.
PTZ-Based SystemsDesigned to expand coverage through mechanical movement, suitable when repositioning latency does not materially increase risk.
Multi-Lens Systems with Active DeterrenceEngineered for environments requiring simultaneous coverage, minimal response latency, and on-site escalation under unattended conditions.
Response Logic and Risk Mitigation
Camera-only and PTZ systems rely on external response workflows and communication latency.
Multi-lens deterrence-enabled systems introduce a local response layer, enabling immediate on-site escalation independent of camera orientation.
Energy Autonomy Impact
Camera-only architectures prioritize extended autonomy with simplified load profiles.
PTZ systems introduce intermittent mechanical loads.
Multi-lens deterrence systems allocate energy across parallel optical channels and event-driven deterrence, making autonomy design and prioritization logic central to reliability.
Operational Complexity and Maintenance Considerations
PTZ systems introduce mechanical wear and alignment dependency.
Multi-lens systems reduce mechanical reliance but require disciplined power-aware control logic.
Integrated deterrence avoids adding standalone alarm devices, which are common long-term failure points in outdoor deployments.
Engineering Decision Summary
Selecting between these architectures is a risk and response strategy decision, not a feature comparison:
✅ Camera-only systems favor simplicity and efficiency
✅ PTZ systems favor flexible coverage with acceptable latency
✅ Multi-lens deterrence systems favor immediacy, redundancy, and unattended reliability
The correct choice depends on response latency tolerance, coverage continuity requirements, and acceptable operational risk.
Operational Reliability & Long-Term Maintenance Logic
Operational reliability is achieved by aligning optical coverage, energy storage, and response activation within defined autonomy boundaries.
By minimizing mechanical actuation and external interfaces, the system reduces wear-related degradation and supports predictable maintenance planning.
Active deterrence operates within controlled duty cycles, ensuring response capability without compromising baseline monitoring functions.
Engineering Decision Q&A
Under what conditions is a multi-lens off-grid surveillance system the correct engineering choice?
When simultaneous multi-directional coverage is required and repositioning latency or blind zones introduce unacceptable risk.
How does active deterrence improve effectiveness in multi-lens systems?
By enabling immediate on-site response independent of camera orientation or operator intervention.
How does energy autonomy influence multi-lens system behavior?
Energy autonomy defines how many optical channels and response functions remain active during extended low-generation periods.
When does simultaneous multi-lens operation become constrained?
Only when cumulative low-irradiance duration exceeds the designed autonomy window, triggering prioritized coverage modes.
Is this system suitable for permanent unattended deployment?
Yes, provided deployment conditions align with defined assumptions regarding solar availability, environmental exposure, and response duty cycles.
Engineering Takeaway
This off-grid solar-powered multi-lens surveillance camera system with active deterrence should be evaluated as a coverage-continuity and response-latency mitigation architecture, not as a camera aggregation.
Its suitability depends on how effectively it balances simultaneous observation, energy autonomy, and event-driven response under real-world operating constraints.